This event is logged at the end of recognition.
Note: The entries in the log are not guaranteed to be sorted by the nbest result at the time when SWIrcnd is printed.
In addition to the Tokens used for every event, this event has the following tokens:
|
Token |
Meaning |
|---|---|
|
BORT |
Beginning of recognition time (when the recognizer first processed the signal). |
|
CONF |
Confidence value for n-best item. Values can range from 0 to 999. |
|
DPNM |
Root name of the diphone acoustic models used to recognize the top choice on the n-best list. (If there is no applicable value to report, a value of NA is used.) |
|
DURS |
Amount of speech processed by the recognizer in milliseconds. The value can sometimes exceed EOSS by small amounts. See Measuring latency with EORT and EOSS. |
|
ENDR |
|
|
EORT |
End-of-recognition time in milliseconds. Clock time when the results are ready. Measured in real time from the arrival of the first packet of the input stream. See Measuring latency with EORT and EOSS. |
|
EOSD |
How much speech data was passed to the endpointer before EOS was determined. This token helps determine latency due to endpointer decision-making (mostly end of speech timeout). If EOSD equals EOSS then something unusual caused the end-of-speech; for example, the maximum speech duration timer expired. See Measuring latency with EORT and EOSS. |
|
EOSS |
End-of-speech signal: where in the input stream the endpointer wanted the recognizer to stop. See Measuring latency with EORT and EOSS. |
|
EOST |
End-of-speech time in milliseconds. Clock time when the endpointer determined the end of caller speech; measured in real time from the arrival of the first packet; delays in the audio path are not counted. See Measuring latency with EORT and EOSS. |
|
GRMR |
Grammar for n-best item. |
|
KEYS |
List of key/value pairs for the top result. |
|
LA |
Value of the swirec_load_adjusted_speedvsaccuracy parameter used for the recognition. Values include: idle "X" values indicate that the parameter specified that value. Values without "X" were determined at runtime with the parameter setting "on." |
|
MACC |
Filename of the statistics file (the monophone accumulator) that tuned the acoustic model used for the recognition event. (Also, see the DACC token). |
|
MDVR |
Model version—version stamp of models. Format is L.M.m.s, where L is language number, M is major version, m is minor version, and s is the set number. |
|
MEDIA |
An audio media type. For example, "MEDIA=audio/basic;rate:8000" |
|
Indicates the acoustic models used for generating the recognition result. Contains a comma separated list showing the language and acoustic model filenames used for first-pass recognition processing to get the top choice on the n-best list. Each list element has the format LangCode/Version/Path/Filename. MPNM=en.us/10.0.0/models/FirstPass/models.hmm,de.de/10.0.0/models/FirstPass/models.hmm |
|
|
NBST |
Number of n-best items. Used only if RSTT is "ok" or "lowconf." |
|
OFFS |
For internal use only. Shows an offset value for acoustic models. For example, "OFFS=1.3". |
|
RAWS |
Raw score for n-best item. |
|
RAWT |
Raw text for n-best item; set to the value of the SWI_literal key. See Measuring latency with EORT and EOSS. |
|
RCPU |
Recognizer CPU time in milliseconds. Measures how much CPU was used for the recognition. |
|
RENR |
|
|
RSLT |
Parsed text for n-best item. |
|
See Return codes. |
|
|
SAFEK |
Parsed text for n-best item. Used only if the grammar sets SWI_safeKey. Typically, the key passes a partial recognition result when passing the whole result might be a security risk. |
|
SCAL |
For internal use only. Shows a multiplier for acoustic scale. For example, "SCAL=5.5". |
|
SECURE |
Indicates that sensitive information is suppressed for this event. The token only appears when true. |
|
SPAG |
The second pass has not modified the result of the first pass. When the recognizer is "unsure" about the accuracy of the nbest list, it invokes a second pass through the data to help improve the accuracy. A second pass uses more CPU and may also presage a low-confidence recognition. |
|
SPIV |
The second pass has been invoked. When the recognizer is "unsure" about the accuracy of the nbest list, it invokes a second pass through the data to help improve the accuracy. A second pass uses more CPU and may also presage a low-confidence recognition. |
|
SPMS |
Second-pass models. Contains a comma separated list showing the language and acoustic model used to recognize the top choice on the n-best list. When this token appears in the log, it confirms the recognizer performed second-pass processing. It does not appear when recognition completes after the first-pass (see MPNM). (Because the n-best can change during the second pass, MPNM and SPMS might not be consistent. For example, they might refer to different languages.) Each list element has the format LangCode/Version/Path/Filename. SPMS=en.us/10.0.0/models/SecondPass1/models1.hmm,de.de/10.0.0/models/SecondPass1/models1.hmm |
|
SPOK |
Normalized raw text for n-best item; set to the value of the SWI_spoken key. See Measuring latency with EORT and EOSS. |
|
WVNM |
Waveform name. |
Below is a sample recognition-end (SWIrcnd) event:
TIME=20010816125814573|CHAN=1|EVNT=SWIrcnd|RSTT=ok|NBST=3|
RSLT=????0130|RAWT=january thirtieth|SPOK=january thirtieth|
GRMR=GURI0|KEYS=<YEAR conf="988">????</YEAR>
<CENTURY conf="988">??</CENTURY><TWO_DIGIT_YEAR conf="988">??
</TWO_DIGIT_YEAR><MONTH conf="988">01</MONTH>
<DAY conf="982">30</DAY><WEEKDAY conf="988">?</WEEKDAY>
<SWI_disallow conf="988">0</SWI_disallow>
<SWI_scoreDelta conf="988">0</SWI_scoreDelta>
<MEANING conf="982">????0130</MEANING>|CONF=982|RAWS=3150|
RSLT=????0131|RAWT=january thirty_first|
SPOK=january thirty_first|GRMR=GURI0|CONF=72|RAWS=1856|
MDVR=1.7.0.0|MPNM=en-us/SpeechPearl|
MACC=noise.intmodels.stats.20021204000834|
DACC=NULL|EOSS=1624|DURS=1624|EOSD=1624|BORT=90|EOST=130|
EORT=891|CPAR=0.315,0.863,-0.223,0.743,0.450,0.156,1.000,0.098|
LA=idle|OFFS=1.3|SCAL=5.5|AWP=1300|FMM=10000|SLM=32|MFP=5000|UCPU=711|SCPU=30
In this case, the recognition engine came up with three possible answers, the top two in separate RSLT tokens. (By default, only the top two results are logged, although NBST=3 in this example. Use swirec_max_logged_nbest to change the number of logged results.) "????0130" was the top n-best result with confidence score (CONF) of 982. Note that the confidence for a particular key can be higher than the overall confidence level for the entire utterance. For example, 01 (month) can have equal or higher confidence than overall confidence level, but not lower.
The key/value pairs for the top result appear in the KEYS token in an XML format. For each key, the confidence score is listed in the "conf" attribute. The SWI_meaning SWI_literal, and SWI_spoken keys are not printed for the KEYS field, since they are printed in the RSLT, RAWT, and SPOK fields, respectively.
For each item on the n-best list, we can identify which active grammar produced it by putting in the appropriate GURIx value, which was specified in the SWIrcst event, into the GRMR field. Thus, we see that the first two results used GURI0 (builtin:date grammar from the SWIrcst example above). If we apply the date grammar to the raw text "january thirtieth," this result is "????0130."
The subtraction EORT–EOSS is a good measure of recognizer latency. This measure does not include additional latency in other parts of the system (for example, speed of audio delivery, application processing of recognition results).
The EOSS–EORT difference is an approximation for latency, and the timings are the products of different components: EORT is reported by the recognizer, and EOSS is reported by the endpointer. When end-of-speech is configured for high accuracy, the recognizer often returns a result before the endpointer completes EOSS process. In these cases, the EOSS-EORT difference is a negative value that indicates zero latency.
Like RAWT, the SPOK token contains the text that was recognized. However, the SPOK text might be written in a normalized form if the grammar was processed with a normalizer before being loaded. For example, if the grammar contains the character string St. Peter the corresponding RAWT text would be "St. Peter" but the SPOK text would be the expanded form "Saint Peter".
The following figure explains relationships among the SWIrcnd timer tokens. Tokens that measure stream time show relative offsets within the audio stream; these are not affected by delays in audio transfer. The tokens that measure signal time reflect the realtime (or clock-time) of the signal, and they are affected by delays.
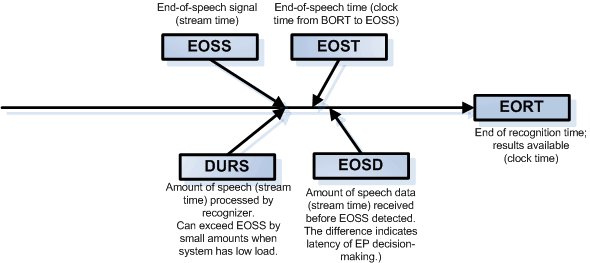
Notes on the figure:
- There can be slight delays between the receipt of the first audio packet and the start of processing (BORT).
- EOSS and DURS are similar: they indicate the length of processed speech in the signal. For reasons described in the footnote, DURS can include small amounts of non-speech after EOSS.
EOSS and DURS can be identical, but DURS can slightly exceed EOSS during periods of low system load. Unless the maximum speech duration or the end-of-speech timer expires, the recognizer does not declare the end-of-speech location until all the audio is received (EOSD). As a result, the recognizer sometimes processes audio data beyond the EOS location (because the processing speed can exceed the audio streaming when the system load is low).
- EOST is always longer than EOSD.
- To measure latency of EP decision-making, use this: EOSD-EOSS
- EORT is especially affected by transfer rates and processing loads. To measure system latency, use this: EORT-EOSS
Reasons for the end of speech (ENDR) include:
|
Return code |
Status |
|---|---|
|
ctimeout |
The end of speech was detected (completetimeout was triggered). |
|
eeos |
External end of speech. The audio sample sent to the recognizer was labeled as the last sample. |
|
itimeout |
Normal end of speech. |
|
maxs |
The maximum speech time was reached (maxspeechtimeout). |
|
nobos |
No beginning of speech detected. |
Reasons for the end of recognition (RENR) include:
|
Return code |
Status |
|---|---|
|
count |
The maximum sentences were reached. (The max is determined by internal algorithms; this is not swirec_max_sentences.) |
|
err |
A system error occurred. |
|
maxc |
The maximum CPU time was reached. |
|
maxsrch |
Recognizer’s maximum allowed search time was reached. |
|
maxsent |
The number of sentences tried. |
|
ok |
Recognition was successful. There is an n-best result. |
|
prun |
Stopped generating the n-best list. This can occur even if no n-best entries returned. One cause is that the pruning threshold was exceeded (swirec_state_beam). But typically, it simply means that there were no more hypotheses to consider. For example, this happens if requesting an n-best size of n but the grammar has fewer than n choices. It will also happen if the recognizer has found a compelling acoustic match so that all the other hypotheses are pruned in the first pass search. |
|
stop |
Recognizer received a stop request. |
Return codes (RSTT) are as follows:
|
Return code |
Status |
|---|---|
|
serr |
A system error occurred. |
|
lowconf |
There was an n-best result (including any possible decoys), but it was below the setting of the confidencelevel parameter. |
|
maxc |
The maximum CPU time was reached (swirec_max_cpu_time). |
|
nomatch |
There was no recognition match, and no n-best result. |
|
ok |
Recognition was successful. There is an n-best result. |
|
stop |
Recognizer received a stop request. |
